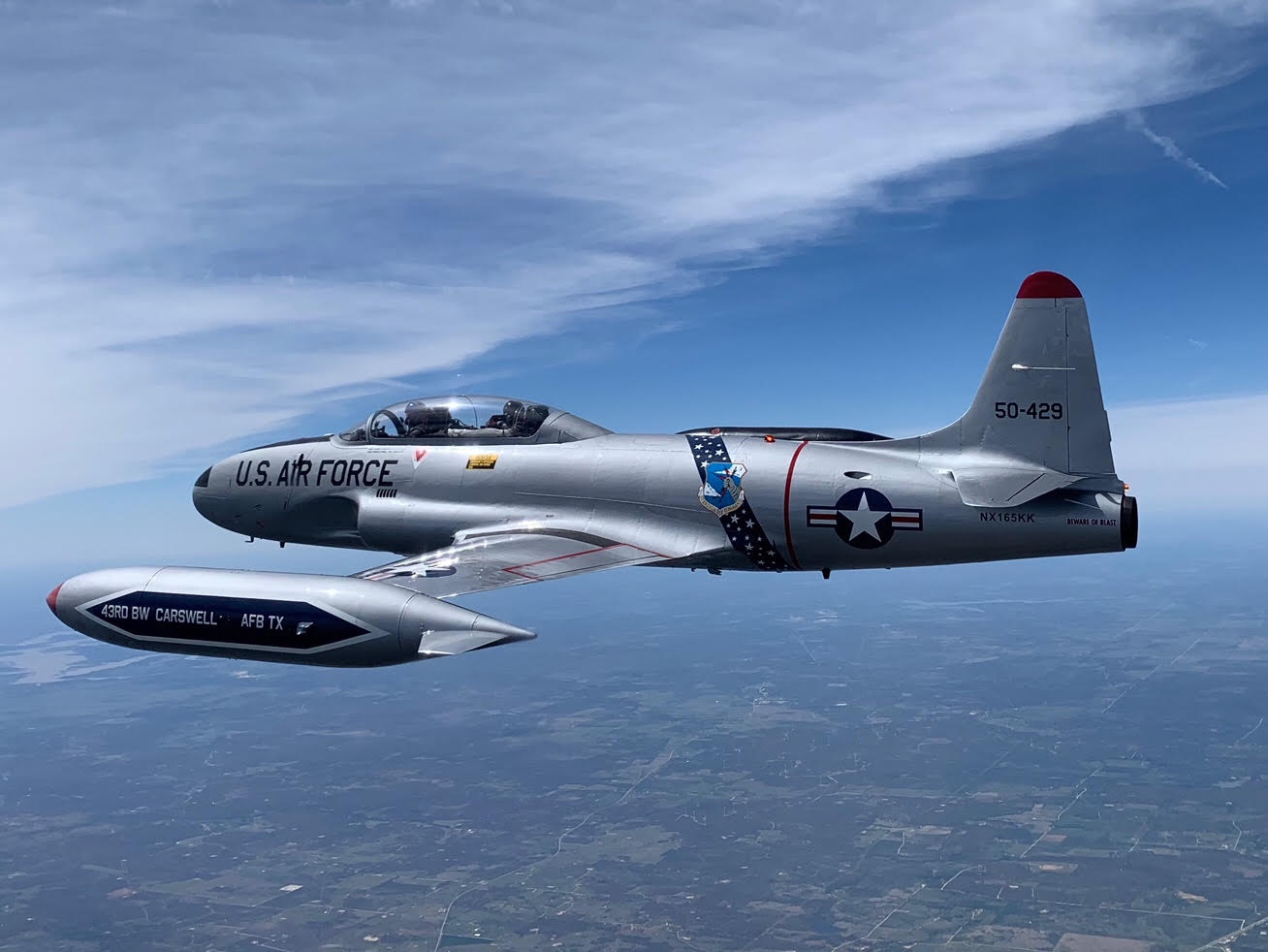
T33 Aircraft - The Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star (or T-Bird) was an American subsonic jet trainer. It was produced by Lockheed and made its first flight in 1948. The T-33 was developed from the Lockheed P-80/F-80, starting with the development of the TP-80C/TF-80C, and later as the T-33A. . It was used by the US Navy initially as the TO-2, later as the TV-2, and after 1962 as the T-33B. Its last operator, the Bolivian Air Force, retired the model in July 2017, after 44 years of service.
The T-33 was derived from the Lockheed P-80/F-80, lengthening the fuselage by about a meter and adding a second seat, instruments and flight controls. It was originally designated as a variant of the P-80/F-80, TP-80C/TF-80C.
T33 Aircraft
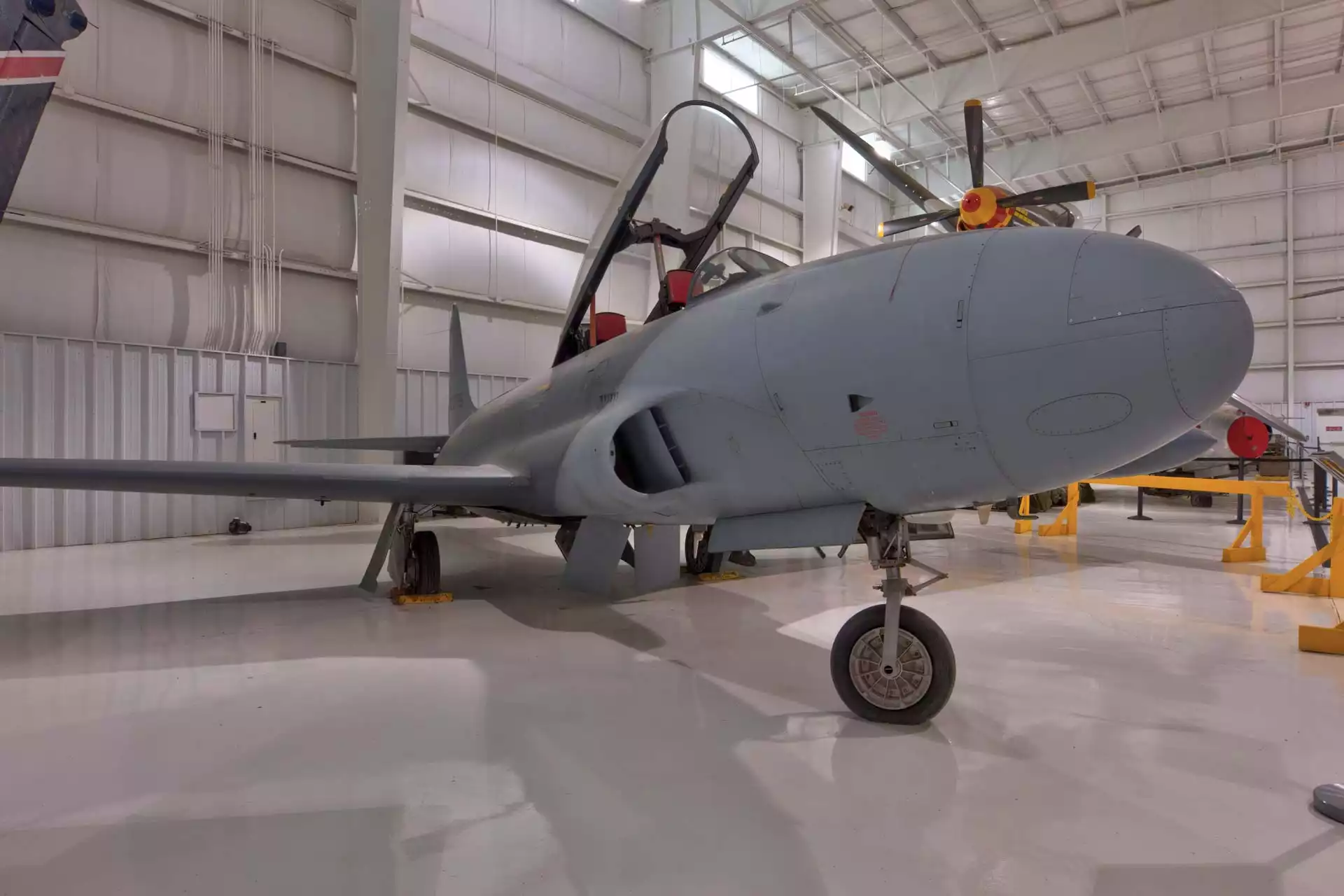

Design work on the Lockheed P-80 began in 1943, with the first flight on January 8, 1944. After the Bell P-59, the P-80 became the first combat aircraft to enter service with the US Army Air Forces. . As advanced aircraft entered service, the F-80 took on a different role: training jet pilots. The T-33 two-seater was designed to train pilots who were already qualified to fly a propeller-driven aircraft.
T33 Shooting Star Jet Trainer Aircraft
Originally designated the TF-80C, the T-33 made its first flight on March 22, 1948, with Lockheed test pilot Tony LeVier at the controls. Lockheed production continued from 1948 to 1959. The US Navy launched the T-33 as a basic trainer in 1949. It was designated the TV-2, but was upgraded to the T-33B in 1962. The P-80C was renamed the TO-1, a year after the TV-1. Lockheed later developed a cruiser version of the P-80/T-33 family, eventually leading to the T2V-1/T-1A SeaStar from the late 1950s through the 1970s. The two TF-80C prototypes served as prototypes for the dual-role all-weather fighter variant that became the F-94 Starfire. A total of 6,557 T-33s were produced, of which 5,691 were produced by Lockheed, 210 by Kawasaki and 656 by Canadair.
The two-seater T-33 was suitable as an advanced trainer, and was used to perform tasks such as drone tracking and target acquisition. The US Air Force began to phase out the T-33 from primary pilot training duties in the command in the early 1960s, when the CSNA T-37 Tweet and the Northrop T-38 Talon began to replace it in the College Pilot. Training. Training Program (UPT). The T-33 was used for cadet training at the Air Force Academy at Peterson Field (now Peterson Air Force Base in Colorado Springs). The T-37 replaced the T-33 in Academy training in 1975. The last T-33 used in advanced training was replaced on February 8, 1967 at Craig AFB, Alabama. A similar transition occurred in the US Navy with the TV-1 (renamed T-33 in 1962), when advanced aircraft such as the North American T-2 Buckeye and the Douglas TA -4 Skyhawk IIs came into play. . USAF and USN versions of the T-33 were used in the 1970s and 1980s as utility aircraft and competition trainers, and some of the older USN aircraft were used for air trials as aerial targets by the Royal Navy. air missiles, and marine surface-to-air missile tests. Several T-33s were assigned to USAF units with the McDonnell F-101, Convair F-102 Delta Dagger and Convair F-106 Delta Dart to support similar Air National Guard units from the Air Defense Command as competitive trainers and the "enemy to practice". "Aircraft. Others later on the F-106 and McDonnell-Douglas F-4 at the Tactical Air Command and Air National Guard units, in the same role, until they finally retired, the last was the NT-33 and He retired. April 1997.
Some T-33s carried two machine guns for marksmanship training, and in some countries the T-33 was even used in combat: the Cuban Air Force used it during the Bay of Pigs invasion, with some losses. The RT-33A version, a reconnaissance aircraft produced mainly for use in foreign countries, had a camera on the nose and additional equipment in the rear cockpit. The T-33 continued to serve as a trainer, reconnaissance drone, combat and tactical simulation training, "mule" aircraft, electronic countermeasures, and combat training and test platforms in the 1980s.
The T-33 served in more than 30 countries and served as a trainer in small air forces. Canadair built 656 T-33s for RCAF/Canadian Forces service as Canadair CT-133 Silver Star, while Kawasaki built 210 in Japan. Other operators were Brazil, Turkey and Thailand, which used the T-33 extensively.
Lockheed P 80 Shooting Star
In the 1980s, attempts were made to modify and modernize the T-33 as the Boeing Skyfox, but a lack of orders led to the cancellation of the project. About 70% of the T-33 airframe was retained in the Skyfox, but powered by two Garrett AiRearch TFE731-3A turbofan engines.
In the late 1990s, 18 T-33 Mk-III and T-33 SF-SCs of the Bolivian Air Force went to Canada to be refurbished by Kelowna Flightcraft. New avionics were installed and an extensive overhaul and refurbishment of the fuselage and wings was carried out. Most of the aircraft returned in early 2001 and operated until the model was officially retired on July 31, 2017, the last military operator.
On June 21, 1996, a T-33A-5-LO (TR-602 trainer) of the Hellenic Air Force, flown by Squadron Leader Ioannis Kouratzoglou, successfully intercepted a Turkish F-16C fighter jet in its airspace. was forbidden in Athens. Altitude, high-g maneuvers.
A limited number of T-33s were purchased privately, with two used by Boeing as follow-on aircraft. In 2010, the Boeing-owned T-33 was used as a follow-up aircraft during the first flight of the Boeing 787.
Aircraft Photo Of N12417
The first flight of the Boeing 737 MAX-7, on March 16, 2018, also included a T-33 follow-up aircraft.
The first flight of the Boeing 777-9, on January 25, 2020, at the same time a follow-up T-33 aircraft, which departed from KBFI and joined the 777-9 at KPAE, stopped at KMWH and again for the 777- Follow 9 on the way back to KBFI, flying around Mount Rainier before landing.
Original US military designation for the Lockheed Model 580 two-seat trainer for the US Army Air Forces. The designation was changed to T-33A on 11 June 1948, following the establishment of the United States Air Force as a separate military service in 1947, and then to T-33A on 5 May 1949; 20 were built.
Two-seat trainer for the US Air Force and for delivery to foreign air forces under the Military Assistance Program, 5,871 were built, including 699 delivered to the US Navy as TV-2s.
T 33 Shooting Star Hi Res Stock Photography And Images
The T-33A conversion was designed for export as a close support version, equipped with undercarriage pods and hardpoints for bombs and missiles. Also used in the original early fighter program at Cannon AFB, NM, circa 1972-75.
This honor was awarded to several T-33As that were converted to UAV targets for the US Navy.
The T-33A was modified as a single-seat reconnaissance version before delivery; 85 were built, mainly for export as part of the Military Assistance Program.

US Navy designation for the P-80C, 50 was transferred to the USN in 1949 as a jet trainer (not technically the T-33 Shooting Star).
Lockheed F 94 Starfire
The US Navy designation for 649 T-33As was diverted from production to the USAF. Two-seat jet terrain training aircraft. The first 28 examples were delivered as TO-2, before the Navy changed the designation to TV-2. On September 18, 1962, the surviving US Navy and Marine Corps aircraft were redesignated the T-33B.
Modified as radio-controlled aerial targets, the TV-2s could be flown as single-seaters in transition flights, later redesignated as the DT-33C.
The T-33AN was a variant of the T-33A powered by Rolls-Royce Nene, for the Royal Canadian Air Force; 656 built by Canadair, with the corporate designation CL-30. The Canadian military designation was later changed from the T-33AN to the CT-133.
An airplane owned by Lockheed, which had a more powerful engine. It was later launched on the T2V SeaStar.
File:lockheed T 33 Shooting Star '69330
An extensive engine overhaul and rebuild project, powered by two Garrett TFE-731 turbofans.
T33 aircraft for sale, kef t33 tweeter, prx t33, t33 filter, prx t33 near me, prx t33 peel, t33 water filter, t33, prx t33 review, prx t33 treatment, yealink t33, t33 filter cartridge











/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/96/bf/96bf0cbc-2916-4467-968e-4bc461e1457d/boeing_n2s.jpg)